The transformer winding deformation tester is a specialized device used to detect the mechanical structural integrity of transformer windings. By analyzing changes in parameters such as inductance and capacitance of the windings, it can determine whether deformation has occurred due to factors such as short-circuit impact, transportation collisions, or long-term overload. Its application scenarios are wide-ranging, covering multiple key aspects of the power system. The following are detailed application scenarios and analysis:
1. Preventive testing of the power system
① Detection of new transformers before operation
a. Scenario: Before a newly manufactured or overhauled transformer is officially put into operation, it is necessary to verify whether the winding structure meets design requirements.
b. Purpose: To eliminate the possibility of winding displacement or deformation caused by vibration and collision during transportation, thereby avoiding operation with defects.
② Regular preventive testing
a. Scenario: According to the "Preventive Testing Regulations for Power Equipment", winding deformation tests are conducted on operating transformers every 1-3 years.
b. Purpose: To detect cumulative deformation of windings at an early stage and prevent sudden failures.
③ Detection after outlet short-circuit impact
a. Scenario: After a transformer encounters a near-field short circuit, the windings may undergo irreversible deformation due to electromagnetic forces.
b. Purpose: To assess the extent of damage to the winding caused by short-circuit impact and decide whether immediate maintenance is required or whether the operation can continue.
2. Fault diagnosis and accident analysis
① Diagnosis of abnormal transformer operation
a. Scenario: When the transformer exhibits non-intuitive faults such as abnormal oil chromatography, enhanced partial discharge, and increased noise.
b. Purpose: To locate the root cause of the fault through winding deformation testing, and to make a comprehensive judgment by assisting with oil chromatography analysis, infrared temperature measurement, and other means.
② Post-accident analysis:
a. Scenario: After accidents such as short circuits and fires occur to transformers, it is necessary to analyze the causal relationship between the deformation and the accident.
b. Purpose: To provide technical basis for accident liability identification and equipment improvement.
3. Application under special operating conditions
① Post-earthquake or geological disaster inspection
a. Scenario: Natural disasters such as earthquakes and floods may cause the transformer foundation to shift or the winding to vibrate.
b. Purpose: To quickly assess the structural integrity of the transformer and decide whether an emergency power outage is required for maintenance.
② Monitoring during transportation
a. Scenario: During long-distance transportation of large transformers, it is necessary to monitor the impact of transportation vibration on the windings.
b. Purpose: To verify the effectiveness of packaging protective measures by comparing test data before and after transportation.
③ Condition assessment of old equipment
a. Scenario: For old transformers that have been in operation for more than 20 years, their remaining lifespan needs to be assessed.
b. Purpose: To assess the degree of insulation aging through winding deformation testing, providing a basis for decisions on extending the lifespan or replacement.
c. Correlation analysis: Comprehensively evaluate the equipment status by combining test results such as insulation resistance and dielectric loss factor.
4. Research and Teaching Field
① Transformer Design Verification
a. Scenario: During the R&D process of a new transformer.
b. Purpose: To verify the design rationality and optimize structural parameters through winding deformation testing.
② Fault simulation experiment
a. Scenario: A power research institution conducts fault simulation experiments such as transformer short-circuit impact and vibration fatigue.
b. Purpose: To study the mechanism of winding deformation and establish a mathematical model correlating the amount of deformation with electromagnetic force and vibration frequency.
c. Data application: Provide experimental evidence for revising the design standards for transformer short-circuit resistance.
③ Teaching and Training
a. Scenario: In vocational colleges or corporate training related to electric power, it is used to demonstrate the internal structure and fault characteristics of transformers.
b. Purpose: To assist students in understanding the impact of winding deformation on transformer performance through actual measurement data, and to enhance their ability to handle faults.
c. Tool: Utilize virtual simulation software to simulate the changes in electrical parameters under different degrees of deformation.
5. Industry-specific Applications
① New Energy Sector
a. Scenario: Transformers in wind power and photovoltaic booster stations need to adapt to operating conditions such as frequent start-stop operations and harmonic interference.
b. Purpose: To detect the deformation risk of windings under harmonic current effects and optimize the design to adapt to the volatility of renewable energy.
② Rail transit field
a. Scenario: subway and high-speed rail traction transformers, which need to withstand frequent short-circuit impacts and vibrations.
b. Purpose: To evaluate the reliability of the winding under extreme operating conditions to ensure driving safety.
③ Industrial special transformers
a. Scenario: Special equipment such as electric furnace transformers and rectifier transformers, which need to withstand the effects of high-order harmonics and DC bias magnetism.
b. Purpose: To detect the deformation trend of windings under non-sinusoidal current, and guide equipment selection and maintenance.
Summary: The application scenarios of transformer winding deformation testers span the entire lifecycle of transformers, from design verification and production quality inspection to operation maintenance and accident analysis, all relying on the critical data they provide. With the development of smart grids and new energy, testers are evolving towards higher frequencies and multi-parameter integration to adapt to more complex operational conditions. Proper selection of testing scenarios and methods can significantly enhance the reliability and economy of transformer operation.
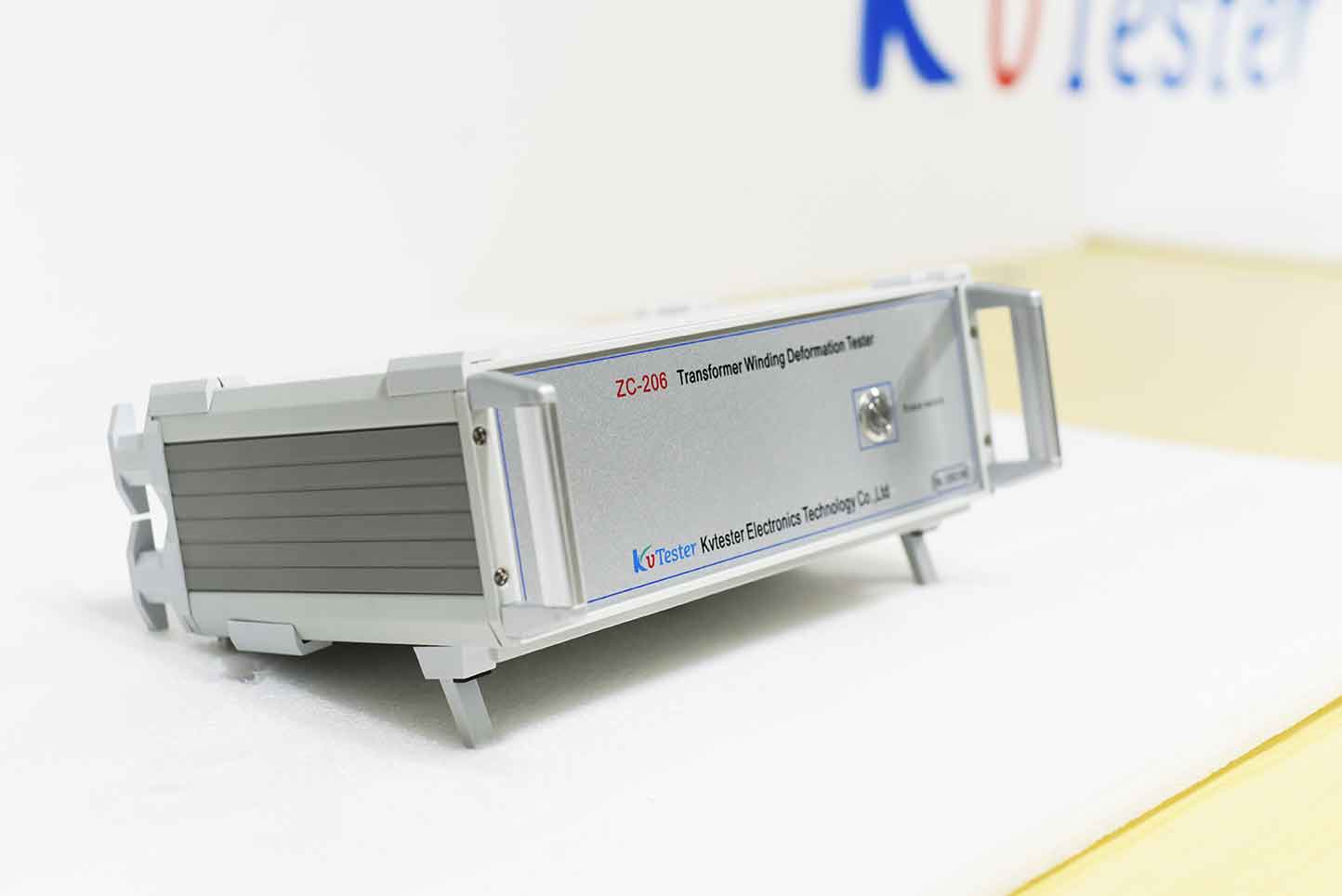

The ZC-206 transformer winding deformation tester quantifies the variation of the winding parameters in different frequency domains, determines the degree of deformation of the winding according to the trend of variation, range, range and frequency response, and then judges whether the transformer is seriously damaged or needs according to the test result. Overhaul. The device is compact and easy to operate.
Kvtester Electronics Technology Co.,Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise specializing in power testing, testing, research and development, production, and sales of testing equipment. It has been engaged in the electrical testing industry for many years, and its products are of high quality. We welcome customers to come and purchase. Service hotline: 0086-27-81778799, to learn more, visit the official website: www.kvtester.com