When testing the transformer ratio, it is necessary to comprehensively control from multiple aspects such as operating specifications, environmental conditions, safety protection, equipment maintenance, and personnel training to ensure the accuracy of the test results and ensure the safety of personnel and equipment. The following are specific precautions and safety measures:
1. Operating standards and preparation before testing
① Verify transformer parameters
Before testing, it is necessary to confirm the information on the transformer nameplate, including rated voltage, wiring group (such as Yyn0, Dyn11), standard value of transformation ratio, etc., to ensure that the test parameter settings are consistent with the actual situation.
Check the appearance of the transformer to ensure there is no damage, oil leakage, or abnormal noise, and avoid testing with defects.
② Choose appropriate testing instruments
Select a ratio tester that matches the range based on the transformer capacity and voltage level to avoid overloading and damage to the instrument.
Priority should be given to intelligent devices with functions such as automatic calibration, error calculation, and group recognition to reduce human operational errors.
③ Standardize the wiring process
Distinguish between high voltage side and low voltage side: strictly follow the instrument manual and transformer nameplate wiring, connect the high voltage side to the high voltage end of the tester, and connect the low voltage side to the low voltage end to avoid reverse connection, which may cause damage to the instrument or test failure.
Phase sequence correspondence: Three phase transformers need to ensure that phases A, B, and C on the high voltage side correspond one-to-one with phases a, b, and c on the low voltage side to avoid triggering alarms due to phase sequence errors.
Good contact: The test pliers need to clamp the transformer terminals to avoid looseness or oxidation that may cause excessive contact resistance and affect test accuracy.
Suspended excess cables: Unused test wires should be suspended to avoid touching metal parts or short circuits.
2. Environmental condition control
① Stay away from sources of interference
The testing site should be kept away from strong electric fields (such as high-voltage lines), strong magnetic fields (such as large motors), and high-frequency equipment (such as radio transmission towers) to prevent power interference from affecting the test results.
Avoid testing in thunderstorm weather or humid environments to prevent the instrument from being affected by moisture or the risk of electric shock.
② Control the ambient temperature
Transformer ratio testers typically require a working environment temperature between -10 ℃ and 50 ℃. Exceeding this range may result in a decrease in instrument performance or damage.
In low temperature environments during winter, the instrument needs to be preheated to normal operating temperature before testing.
③ Maintain good ventilation
The testing site needs good ventilation to avoid the aging or failure of internal components caused by prolonged high-temperature operation of the instrument.
3. Safety protection measures
① Personal protective equipment
Operators are required to wear insulated gloves, insulated shoes, and safety helmets to prevent electric shock or injury from falling objects.
When testing on the high-voltage side, it is recommended to wear protective clothing to avoid arc burns.
② Equipment grounding protection
The tester must be reliably grounded with a grounding resistance of less than 4 Ω to prevent electric shock to personnel or damage to the instrument caused by leakage.
The grounding wire should use a dedicated grounding rod to avoid using rusty or broken grounding wires.
③ Power off operation and verification
Before testing, all power sources on the high and low voltage sides of the transformer must be disconnected, and a "Do not close" warning sign must be hung.
After confirming that there is no electricity using a voltage tester, wiring operations can be carried out.
④ Prevent reverse power transmission
If the transformer is operated in parallel with other equipment, all parallel branches must be disconnected before testing to prevent reverse power transmission from causing damage to the instrument or electric shock to personnel.
⑤ Set up a safety fence
Set up safety fences or warning tapes around the testing site to prohibit non operators from entering and prevent accidental contact with live equipment.
4. Testing process monitoring and emergency response
① Real time monitoring of instrument status
During the testing process, it is necessary to closely observe the instrument screen display. If there are alarms such as "overcurrent protection" or "wiring error", the testing should be stopped immediately and the cause should be investigated.
Avoid prolonged continuous testing to prevent instrument overheating and damage.
② Emergency Response Plan
If an electric shock accident occurs, the power supply should be immediately cut off, and an insulating object (such as a dry wooden stick) should be used to separate the electrocuted person from the charged body. First aid measures such as cardiopulmonary resuscitation should be taken, and 120 should be called for help.
If the instrument emits smoke or catches fire, quickly cut off the power and use a dry powder fire extinguisher to extinguish the fire. It is forbidden to use water to extinguish the fire.
5. Maintenance and recording after testing
① Equipment cleaning and maintenance
After the test is completed, use a dry soft cloth to wipe the surface of the instrument to prevent dust or moisture from entering.
Check if the test line is damaged, and replace it promptly if there is any damage.
② Data recording and analysis
Record in detail the testing time, ambient temperature, transformation ratio, error percentage, and other data, and compare them with historical data to analyze the trend of transformer performance changes.
If the test results are abnormal, it is necessary to further investigate faults such as transformer winding deformation and inter turn short circuit.
③ Instrument repositioning and storage
Return the testing instrument, testing line, testing pliers and other tools to the dedicated toolbox to avoid loss or damage.
The instrument should be stored in a dry, ventilated, and non corrosive gas environment, avoiding direct sunlight or high temperature baking.
6. Personnel training and qualification requirements
① Professional training
Operators need to receive training on the use of transformer ratio testers, familiarize themselves with the instrument's functions, operating procedures, and safety regulations.
Regularly organize safety drills to improve emergency response capabilities.
② Work with certification
Operators involved in high-voltage testing must hold a high-voltage electrician certificate to ensure professional operation qualifications.
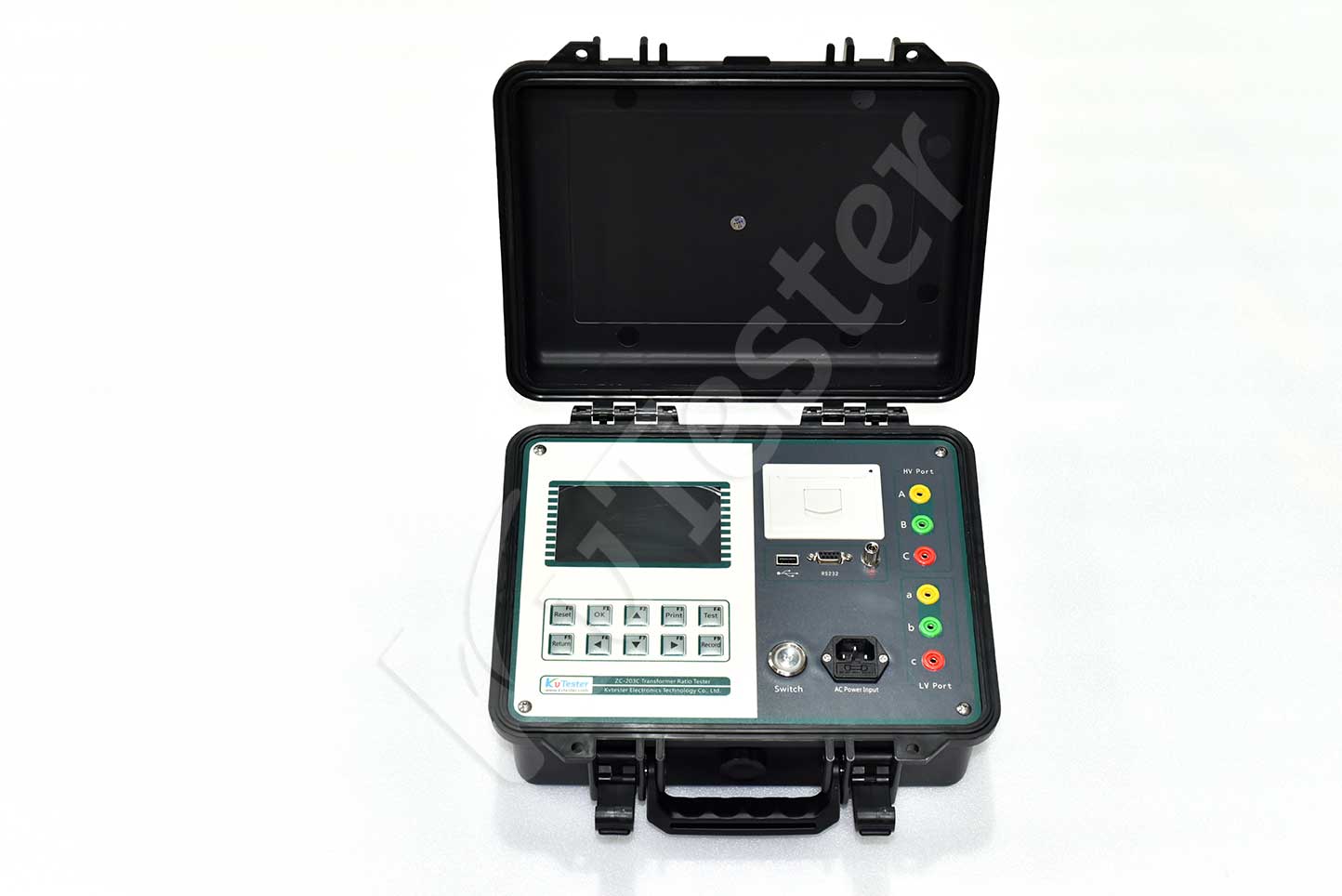

Kvtester Electronics Technology Co.,Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise specializing in power testing, testing, research and development, production, and sales of testing equipment. It has been engaged in the electrical testing industry for many years, and its products are of high quality. We welcome customers to come and purchase. Service hotline: 0086-27-81778799, to learn more, visit the official website: www.kvtester.com