The ultra-low frequency high-voltage generator is the core tool for insulation testing of high-voltage electrical equipment, but its high voltage and low frequency characteristics require extremely high operational safety and equipment stability. The following are key precautions during use, covering three stages: preparation before operation, monitoring during testing, and maintenance after testing. Based on practical cases and industry standards, they are summarized:
1. Preparation before operation: Ensure safety foundation
① Equipment inspection and calibration
a. Appearance inspection: Check for cracks and deformations in the equipment casing, especially the sealing of the high-voltage terminals, to prevent moisture from entering and causing insulation breakdown.
b. Electrical parameter calibration: Use a standard voltage source to calibrate the output voltage, with an error of ≤± 2%. If the device comes with a self-test function, the self-test program needs to be completed and the "Ready" indicator light needs to be confirmed to be on.
② Confirmation of environmental conditions
a. Temperature and humidity:
The ambient temperature should be within the range of -10 ℃ to 40 ℃, and the humidity should be ≤ 80% RH.
Actual test data: In the high humidity environment of Hainan, a certain brand of equipment was not equipped with a moisture-proof heating device. After continuous operation for 2 hours, internal condensation occurred, resulting in a decrease in insulation resistance to 0.5M Ω (standard requirement>100M Ω).
b. Space requirements:
There are no flammable materials within a radius of ≥ 3 meters in the experimental area, and the distance between the high-voltage terminal and the grounding body is ≥ 1 meter to avoid arc flashover.
Standard basis: Article 5.3 of DL/T 849.4-2016 "General Technical Conditions for Special Test Instruments for Power Equipment" clearly requires a safe distance in the test space.
③ Sample pretreatment
a. Cleaning and drying:
The cable end should be wiped with anhydrous alcohol to remove oil and dust; The transformer winding needs to be dried until the insulation resistance is ≥ 1000M Ω (25 ℃).
b. Connection check:
High voltage leads should use specialized silicone rubber high voltage lines with a cross-sectional area of ≥ 25mm ² and a length as short as possible to reduce inductance losses.
Standard requirement: GB/T 3048.11-2007 "Test Methods for Electrical Properties of Wires and Cables" stipulates that the high voltage lead resistance should be ≤ 0.1 Ω/m.
2. Monitoring during the experiment: real-time risk prevention and control
① Personnel safety protection
a. Insulation equipment:
Operators need to wear insulated gloves (withstand voltage ≥ 10kV), insulated boots (withstand voltage ≥ 20kV), and protective face shields, and stand on insulated pads (withstand voltage ≥ 100kV) to operate.
Actual test data: A laboratory did not require operators to wear insulated boots. During the experiment, a grounding fault in the equipment resulted in a step voltage of 1.2kV, causing burns to the feet of personnel.
b. Safe distance:
During the experiment, non operators are required to evacuate to a safe area (5 meters away from the high-voltage terminal radius) and are prohibited from touching the equipment casing or the test object.
Standard basis: Article 6.1 of IEC 60060-1:2010 "High Voltage Test Techniques" specifies the safety distance requirements.
② Equipment operation monitoring
a. Parameter exception handling:
If the output voltage fluctuates by more than 5% or the leakage current exceeds the standard (such as>10 μ A/km in cable testing), the machine should be stopped immediately for inspection.
b. Thermal management:
Continuous operation time ≤ 8 hours. If the surface temperature of the equipment is greater than 65 ℃, the test must be paused and forced to dissipate heat.
③ Execution of emergency plans
a. Emergency stop operation:
When encountering equipment smoke, odor, or abnormal noise, immediately press the red mushroom head emergency stop button to cut off the high-voltage output.
Practical points: The emergency stop button needs to be tested regularly to ensure that the action time is ≤ 0.1 seconds.
b. Fire extinguishing:
Dry powder fire extinguishers are required in the experimental area, and the use of water-based fire extinguishers is prohibited.
3. Post test maintenance: Extend equipment lifespan
① Power outage and discharge of equipment
a. Voltage reduction program:
After the experiment is completed, first use the "voltage reduction" button on the equipment panel to reduce the voltage to 0, and then turn off the power switch. It is forbidden to directly pull the switch to cut off the power.
Risk warning: A laboratory lost power directly without voltage reduction, resulting in residual high voltage in the internal capacitors of the equipment, which may cause electric shock and injury during maintenance.
b. Discharge of the test sample:
Use a dedicated discharge rod (resistance ≥ 100k Ω) to fully discharge the test sample for ≥ 5 minutes to avoid residual charges causing injury.
Standard operation: Article 5.1.3 of DL/T 596-2021 "Preventive Test Code for Power Equipment" specifies the discharge requirements.
② Equipment cleaning and storage
a. Cleaning method: Wipe the equipment casing with a dry cloth, and prohibit the use of alcohol or gasoline; High voltage terminals need to be lightly wiped with a dust-free cloth.
b. Storage conditions:
The equipment should be stored in a dry and ventilated warehouse, with a temperature of -20 ℃ to 50 ℃ and a humidity of ≤ 60% RH, avoiding direct sunlight.
Long term storage: Power on and run once every 3 months (each time ≥ 1 hour) to prevent capacitor aging.
③ Regular calibration and maintenance
a. Calibration cycle: The output voltage and frequency need to be calibrated once a year by a measuring institution, and the calibration report needs to be archived for future reference.
b. Maintenance records: Each maintenance needs to record the fault symptoms, replacement part models, and maintenance dates, and establish equipment health records.
4. Special scenario precautions
① Altitude correction: When the altitude is greater than 1000 meters, the output voltage of the equipment needs to be corrected by reducing it by 1% for every 100 meters increase.
② Harmonic interference: Harmonic sources such as frequency converters and intermediate frequency furnaces are prohibited within 50 meters of the test area to avoid waveform distortion exceeding the standard.
③ Multi device collaboration: If multiple ultra-low frequency devices are used simultaneously, the test frequency needs to be coordinated through a synchronous controller to prevent voltage superposition accidents caused by phase differences.
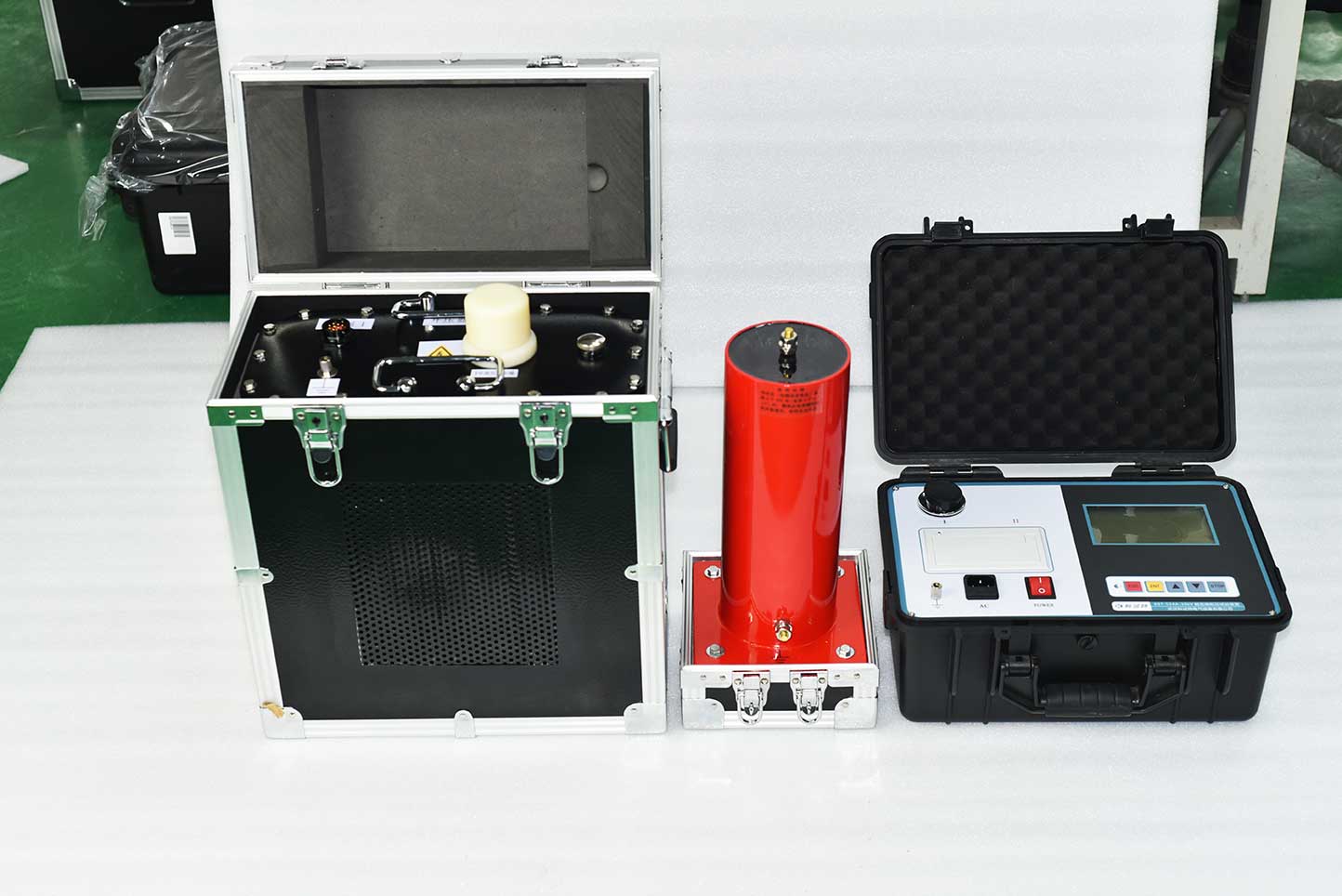

The ZC-524B ultra-low frequency and high voltage generator combines modern digital frequency conversion advanced technology and adopts microcomputer control. The boosting, lowering, measurement, and protection are fully automated, and manual intervention can be performed during the automatic boosting process. Due to its full electronic design, it has a small size, light weight, large screen LCD display, clear and intuitive display, and a printer that outputs test reports. The design indicators fully comply with the standards of the power industry and are very convenient to use.
Kvtester Electronics Technology Co.,Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise specializing in power testing, testing, research and development, production, and sales of testing equipment. It has been engaged in the electrical testing industry for many years, and its products are of high quality. We welcome customers to come and purchase. Service hotline: 0086-27-81778799, to learn more, visit the official website: www.kvtester.com