The transformer voltage ratio refers to the ratio of the line voltage between the primary winding and the secondary winding during no-load operation. The purpose of measuring the transformer voltage ratio is to:
1. Check the correctness of the turns ratio of the transformer winding.
2. Check the condition of the tap.
3. When a transformer malfunctions, it is common to measure the transformer ratio to check for inter turn short circuits.
4. Check if the transformer tap is welded incorrectly.
5. Check if the transformer has been damaged or changed during transportation.
6. Determine whether the transformer can operate in parallel.
When transformers are operated in parallel, ideally there is no circulating current between them. However, in reality, due to errors in transformer ratio and unbalanced loads on the parallel operation bus, there is circulating current between the parallel operation transformers, but it does not affect the normal operation of the transformers. If the transformer gear is not adjusted properly during voltage adjustment, a large circulating current will form between the parallel operation transformers, causing the transformers to overheat and endangering their insulation, which is even more detrimental to the safe and economical operation of the transformers. According to the power industry standard DL/T 596-2021, there is no significant difference in the voltage ratio of each tap compared to the nameplate value, and it conforms to the rules. The allowable deviation of voltage ratio error for transformers below 35kV with a voltage ratio less than 3 is ± 1%. The allowable deviation for the rated tap voltage ratio of all other transformers is ± 0.5%. The voltage ratio of other taps should be within one tenth of the impedance voltage value (%) of the transformer, but the deviation should not exceed ± 1%.
When measuring the transformation ratio of a transformer, first apply a low voltage on the high or low voltage side of the transformer, with a value of 1-25% of the rated voltage, and then measure the voltage on the other side with an instrument or transformer. Determine whether each winding of the transformer has the rated voltage specified in the technical specifications through calculation. When measuring with an AC voltmeter, the accuracy of the instrument should be at level 0.5. When using a voltage transformer for measurement, the accuracy of the transformer should be at level 0.2, and the measured voltage value should be selected as much as possible between 80% and 110% of the rated voltage of the transformer. In addition, using a transformer ratio tester for measurement is more convenient as it can directly measure the transformer ratio.
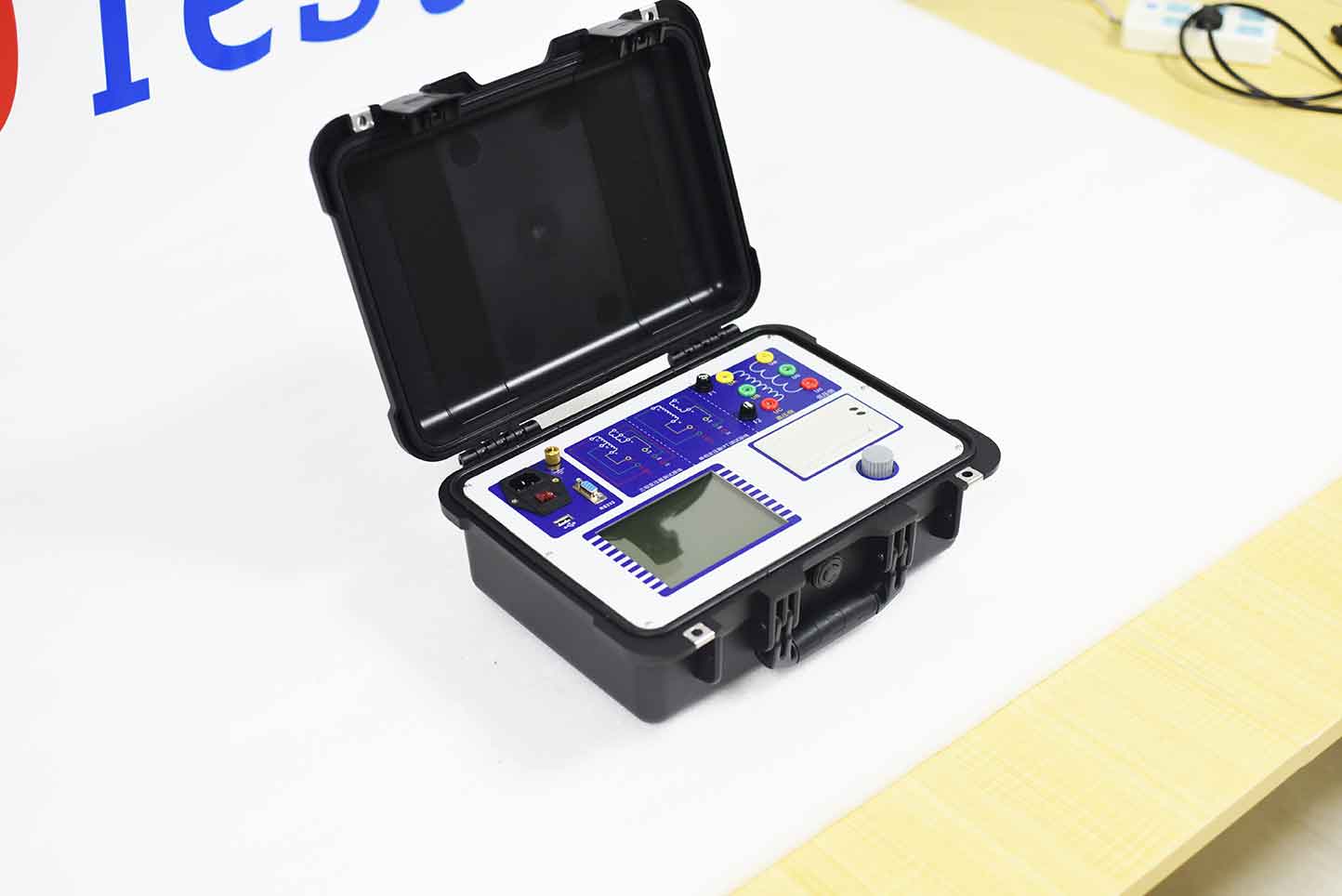

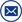
The ZC-203A fully automatic transformer ratio group tester is mainly used to supervise the quality of transformer products during factory delivery and use, prevent inter turn short circuits, open circuits, connection errors, internal faults or contact faults of voltage regulating switches. The instrument is easy to operate, has complete functions, stable and reliable data, fast testing speed, and can meet the needs of various large, medium, and small transformer ratio tests. It is an ideal testing instrument for the power industry sector.
Kvtester Electronics Technology Co.,Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise specializing in power testing, testing, research and development, production, and sales of testing equipment. It has been engaged in the electrical testing industry for many years, and its products are of high quality. We welcome customers to come and purchase. Service hotline: 0086-27-81778799, to learn more, visit the official website: www.kvtester.com