The common causes of faults in dielectric loss testers can be summarized as follows:
1. Poor contact
① Poor hook contact: When using a hook to connect the test sample during on-site measurement, if there is poor contact between the hook and the test sample, the discharge at the contact point will cause serious fluctuations in the data. Especially when there is an oxide layer on the surface of the test sample or when it is shaken by wind, it is easy to cause poor contact.
② Poor grounding contact: Poor grounding can cause serious fluctuations in instrument protection or data. Ensure that the grounding point is free of impurities such as paint and rust, and ensure zero resistance grounding.
2. Environmental factors
① Excessive air humidity: The measurement of dielectric loss is abnormally increased (or decreased, or even negative) and unstable due to the high air humidity. In high humidity environments, moisture will diffuse into the interior of the material, increasing its conductivity and leading to an increase in the dielectric loss factor.
② Temperature effect: Although the direct impact of temperature on the dielectric loss tester may not be as significant as humidity, changes in temperature can also affect the accuracy of test results. It is usually recommended to conduct testing within a suitable temperature range.
3. Power supply issue
① Unstable generator power supply frequency: When using a generator for power supply, unstable input frequency can affect the accuracy of test data. At this point, the fixed frequency 50Hz mode can be used to ensure the stability of the input frequency.
4. Test line issues
① Test line damage: Long term use or improper operation may result in hidden open circuits, short circuits between core wires and shields, or poor contact of plugs in the test line. These issues will affect the accuracy of the test data.
② Poor plug contact: If the plug of the test line has poor contact, it can also cause unstable or interrupted data transmission.
5. Instrument malfunction
① Internal component damage: Electronic components such as capacitors and resistors inside the dielectric loss tester may be damaged due to aging, overheating, or voltage surges, causing the instrument to malfunction.
② Power supply issue: Unstable or excessively high or low input power may affect the normal operation of the instrument. Ensure that the input power is within the range specified by the instrument.
③ Poor grounding: In addition to poor grounding of the test sample, poor grounding of the instrument itself may also cause data abnormalities or instrument protection.
6. Wrong selection of working mode
① Improper selection of measurement mode: Choosing the wrong measurement working mode (such as positive wiring, reverse wiring, CVT mode, etc.) after wiring can result in inaccurate test data. The appropriate measurement mode should be selected based on the test sample and testing requirements.
7. The impact of experimental methods
Improper testing method: The measurement results of the dielectric loss tester are greatly affected by the testing method. If the testing method is improper or does not consider the characteristics of the equipment, it may result in inaccurate test data or inability to reflect the true condition of the equipment.
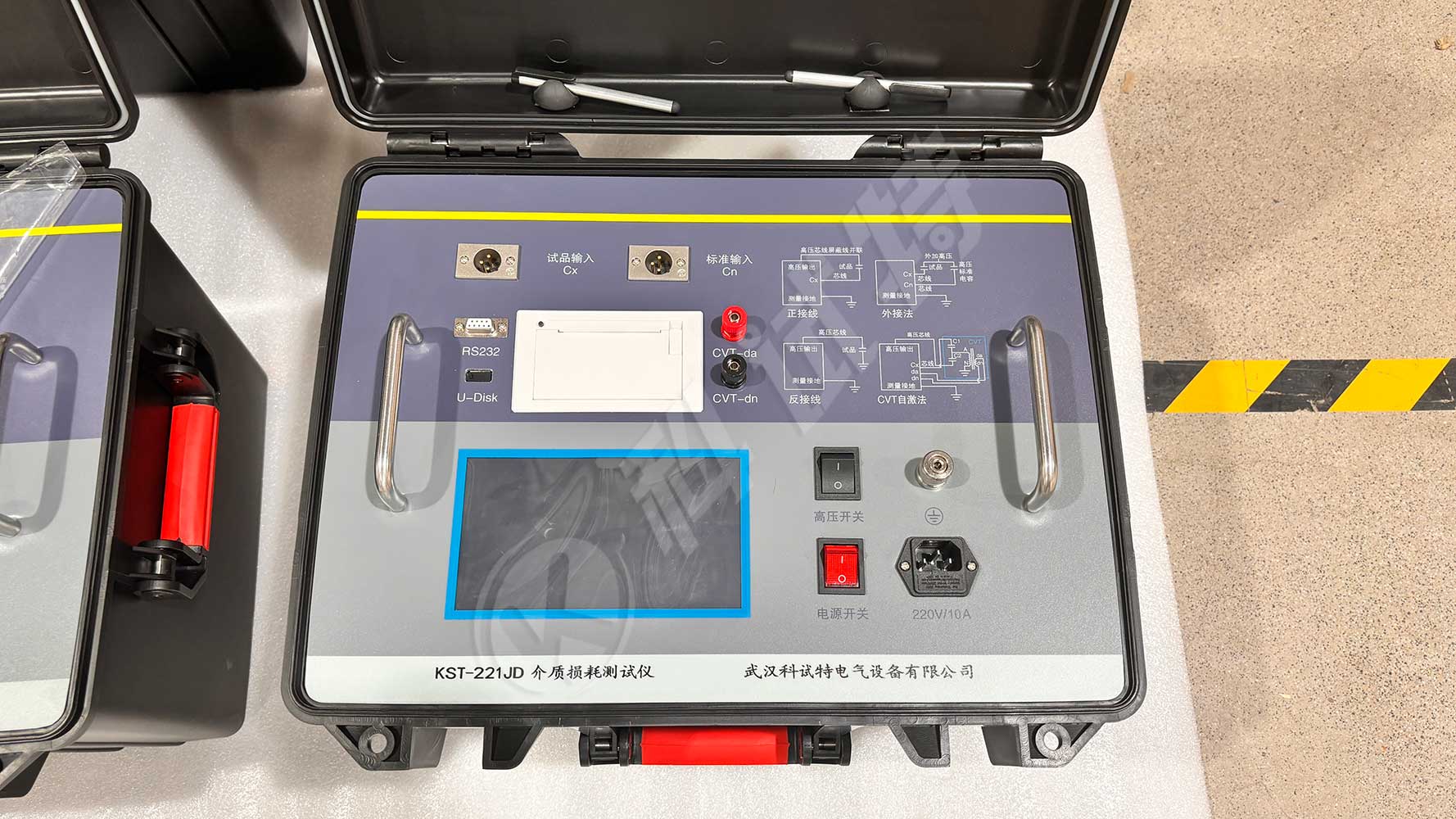

Kvtester Electronics Technology Co.,Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise specializing in power testing, testing, research and development, production, and sales of testing equipment. It has been engaged in the electrical testing industry for many years, and its products are of high quality. We welcome customers to come and purchase. Service hotline: 0086-27-81778799, to learn more, visit the official website: www.kvtester.com