1、 Sources of Partial Discharge Interference
The generalized partial discharge interference refers to not only the interference that enters the monitoring system through the current sensor along with the partial discharge signal, but also the interference that affects the monitoring system itself, such as grounding, shielding, and interference caused by improper circuit processing. On site partial discharge interference specifically refers to the former, which can be divided into continuous periodic interference, pulse interference, and white noise. Periodic interference includes system harmonics, carrier communication, and radio communication. Pulse type interference is divided into periodic pulse type interference and random pulse type interference. Periodic pulse type interference is mainly caused by high-frequency inrush currents generated by the operation of power electronic devices. Random pulse type interference includes corona discharge on high-voltage lines, partial discharge generated by other electrical equipment, discharge generated by tap changer action, arc discharge generated by motor operation, suspended potential discharge generated by poor contact, etc. White noise includes coil thermal noise, ground grid noise, and various noises coupled into power supply lines and transformer relay protection signal lines.

2、 Classification of Partial Discharge Interference
The interference caused by various reasons will seriously affect the partial discharge test. If these interferences are continuous and their amplitude is basically the same (background noise), they will reduce the effective sensitivity of the detector, that is, the minimum visible discharge amount is greater than the theoretical minimum value of the test circuit used. This form of interference increases with voltage, so the sensitivity decreases proportionally. In other cases, the discharge that occurs in the test circuit as the voltage increases can be considered to occur inside the test sample. Therefore, it is important to minimize interference and use a detector with actual discharge waveform display to identify false interference discharge responses from the interference discharge of the sample as much as possible. According to the location of possible interference sources in the measurement test circuit, interference sources can be divided into two categories: the first type is interference unrelated to the magnitude of the applied high voltage, and the second type is interference generated only when the high voltage is applied to the circuit.
The main forms of interference are as follows:
1. The interference from the power supply may affect the measurement as long as the control part, Pressure regulator and transformer are connected (without boosting);
2. Interference from the Earthing system usually refers to the interference deflection caused by the potential difference of different grounding points on the measuring instrument in case of poor grounding connection or multiple grounding;
3. Interference detected from other high-voltage tests or electromagnetic radiation, which is caused by the electromagnetic coupling of external electromagnetic fields in the circuit, including radio frequency interference from radio stations, interference from adjacent high-voltage equipment, fluorescent lamps, welding, arc or spark discharge;
4. Discharge of the test circuit;
5. Contact noise caused by poor contact within the test circuit or sample.

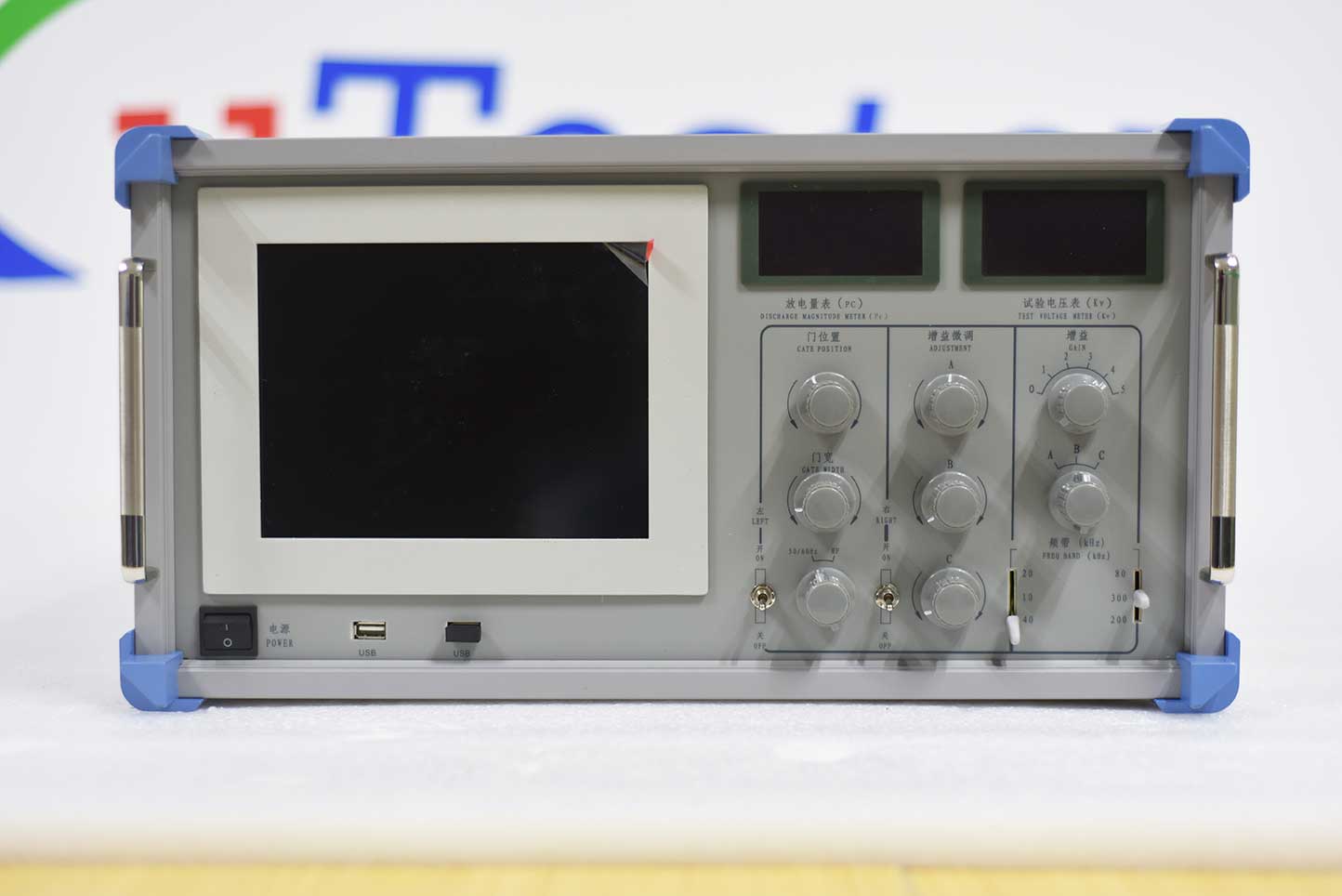
KST-254 four channel partial discharge detector has independent four channels. It uses Solid-state drive, humanized selection of front and rear four channel electrical signal channels, new integrated motherboard, high frequency, use of high-speed acquisition card, more stable, detection sensitivity increased to 0.05pC, sampling rate per channel 80MHz, large size LCD touch screen, Bluetooth wireless transmission, rich peripheral interfaces, A lighter body is more suitable for mobile use in complex environments. Suitable for AC and DC partial discharge detection and positioning of transformers, reactors, generators, transformers, bushings, GIS, lightning arresters, high-voltage switches, switchgear, and other high-voltage electrical equipment. Widely used in high-voltage electrical equipment manufacturers, power electronics high-tech enterprises, power supply companies across the country, and power science research institutes and other units.