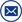
Transformer is a very important part in power engineering construction. We often hear dry-type transformer (referred to as dry transformer) and oil immersed power transformer (referred to as oil transformer). What is the main difference between dry-type transformer and oil immersed power transformer in power engineering construction? What are their advantages and disadvantages?
The biggest difference between oil immersed power transformer and dry-type transformer is "oil". Since oil is liquid and has fluidity, oil immersed power transformers must have enclosures. Inside the casing is transformer oil, which is immersed in the coil of the transformer. The coil of the transformer cannot be seen from the outside. The dry-type transformer has no oil-free shell, and the coil of the transformer can be directly seen;

They are power transformers, and the magnetic circuit will have an iron core to make the winding of the circuit. The biggest difference is "oily" and "dry". In other words, the cooling medium of the two is different. The former uses transformer oil (e.g β Oil) as a cooling and insulating medium which uses air or other gases such as SF6 as a cooling medium. Oil change is to put the body composed of iron core and winding into the oil tank filled with transformer oil. The core and winding are usually wrapped with epoxy resin for drying. There is also a non encapsulated type in use today. The winding is impregnated with special insulating paper to prevent the winding or iron core from being damp. In order to facilitate heat dissipation, that is, for the convenience of internal insulation oil flow, a heat sink is designed outside the oil immersed power transformer, just like a heat sink. The dry-type transformer does not have this radiator, and the heat is cooled by the fan under the transformer coil. Oil immersed power transformers are usually installed in indoor or outdoor independent transformers for fire protection. The dry-type transformer must be installed indoors, generally in the distribution room.
In terms of output and capacity, the current dry voltage level is only 35kV. Its capacity is smaller than that of oil change, about 2500kVA. Moreover, since the manufacturing process of the dry-type transformer is more complicated and costly than that of the oil type transformer with the same voltage level and capacity, the oil type transformer still has more oil. However, due to the advantages of environmental protection, flame retardancy and impact resistance, dry transformer is often used in indoor power supply and distribution places with high requirements, such as hotels, office buildings and high-rise buildings.
It can be seen that dry-type transformer and oil type transformer have their own advantages and disadvantages. Oil type transformer has low cost and convenient maintenance, but it is flammable and explosive. Dry type transformer can be installed in the center of load due to its good fire resistance to reduce voltage loss and power loss. However, the dry-type transformer is expensive, bulky, moisture-proof, dust-proof and noisy.

Next, we summarize the differences mentioned above into the following seven points:
1. Appearance
These two appearances are different. Dry type transformer can directly see the core and coil, while oil immersed power transformer can only see the shell of the transformer;
2. Different lead forms
Silicone rubber bushing is used for dry-type transformer, and porcelain bushing is used for oil immersed power transformer;
3. Different capacities and voltages
Dry type transformers are generally suitable for power distribution. Most of the capacity are below 2000kVA, the voltage is 10kV and below, and some can reach 35kV voltage level; The oil immersed power transformer can reach all the required capacity, and the voltage level can also reach all the voltages; Oil immersed power transformers must be used in the UHV 1000kV lines under construction in China.
4. Insulation and heat dissipation are different
Dry type transformers generally adopt resin insulation, rely on natural air cooling and large capacity fan cooling; The oil immersed power transformer is insulated with insulating oil, and the internal coil of the transformer is cooled by the circulating use of the insulating oil inside the transformer.
5. Applicable place:
Dry type transformers are mostly used in places requiring "fire protection and explosion-proof", and should be used in general large buildings and high-rise buildings; Oil immersed power transformers are mostly used in places where "accident oil pool" is excavated due to oil gushing or oil leakage after an outdoor "accident".
6. Different bearing capacity
Generally, dry-type transformer shall operate under rated capacity, while oil immersed power transformer has better overload capacity.
7. Different costs
For transformers with the same capacity, the purchase price of dry-type transformers is much higher than that of oil immersed power transformers.